Introduction
In recent years, the intersection of insurance and blockchain technology has paved the way for significant innovations in claims processing. One of the most promising developments is the use of smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They facilitate and automate the execution of processes, including claims processing, without the need for intermediaries. This article explores how smart contracts are transforming insurance claims processing, their benefits, challenges, and future implications.
Understanding Smart Contracts in Insurance
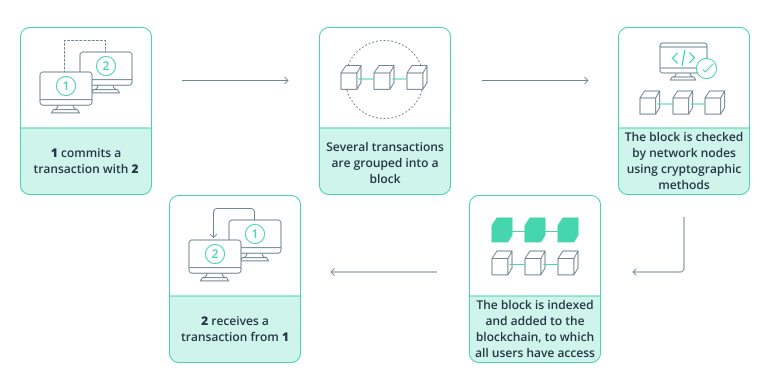
Smart contracts are computer programs stored on a blockchain that automatically execute actions when predetermined conditions are met. In insurance, these contracts can automate various processes, such as policy issuance, premium payments, and crucially, claims processing. Traditional claims processing involves multiple steps, human intervention, and can be prone to delays and disputes. Smart contracts aim to streamline this process by encoding the terms of the insurance policy and automating claims validation and payouts.
Key Components of Smart Contracts in Claims Processing
- Policy Terms and Conditions: Smart contracts include the policy’s terms and conditions, defining the coverage, exclusions, and other relevant details.
- Claims Submission: Policyholders submit claims through an interface linked to the smart contract, providing necessary documentation and evidence.
- Claims Verification: The smart contract verifies claims against predefined conditions, such as policy coverage and validity.
- Automated Payouts: Upon verification, the smart contract triggers automatic payouts to the policyholder’s account.
- Transparency and Security: All transactions and contract terms are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of fraud.
Benefits of Smart Contracts in Insurance
- Efficiency: Claims processing can be significantly faster and more efficient with smart contracts, reducing administrative costs and improving customer satisfaction.
- Accuracy: Automation minimizes human error in claims processing, ensuring that payouts are based strictly on the terms encoded in the contract.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology provides an immutable record of transactions, enhancing transparency and trust between insurers and policyholders.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, smart contracts can lead to cost savings for insurers, which may be passed on to policyholders.
Challenges and Considerations
While smart contracts offer compelling advantages, several challenges must be addressed:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Insurance regulations vary globally and may not yet accommodate smart contract technology fully.
- Complexity: Developing smart contracts requires specialized knowledge of both insurance operations and blockchain technology.
- Security Risks: While blockchain technology enhances security, smart contracts are not immune to vulnerabilities or hacking.
- Scalability: Blockchain networks must handle significant transaction volumes to support widespread adoption in the insurance industry.
Use Cases and Examples
Several insurance companies and startups are already exploring or implementing smart contract technology:
- Parametric Insurance: Smart contracts can automatically trigger payouts based on predefined triggers, such as weather data for crop insurance.
- Flight Delay Insurance: Policyholders can receive automatic payouts if their flight is delayed beyond a certain threshold, verified through data from flight-tracking services.
- Health Insurance: Claims for specific medical conditions can be automatically verified against predefined medical records and treatment protocols.
Future Directions
The future of smart contracts in insurance looks promising but requires collaboration between insurers, regulators, and technology providers. Key areas for development include:
- Interoperability: Ensuring smart contracts can communicate and operate across different blockchain platforms and insurance systems.
- Standardization: Establishing industry standards for smart contract development, execution, and auditing.
- Integration with AI and IoT: Combining smart contracts with artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to automate claims verification further.
Conclusion
Smart contracts represent a transformative technology in insurance claims processing, promising efficiency, transparency, and cost savings. While challenges remain, ongoing developments and collaborations are paving the way for broader adoption across the insurance industry. As regulatory frameworks evolve and technology advances, smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize how insurance claims are managed, benefiting both insurers and policyholders alike.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of how smart contracts are reshaping insurance claims processing, emphasizing their benefits, challenges, and future potential. As this technology continues to evolve, its impact on the insurance industry will undoubtedly be profound, ushering in a new era of efficiency and trust in claims management.